Cost-effective Method to Quickly Produce and Purify Large Quantities of Biologically Active ncRNAs
Abstract
Researchers at the University of California, Davis have developed a method to develop and purify large quantities of ncRNA for basic and translational research, as well as for therapeutics delivery.
Full Description
The discovery of the role of chimeric, non-coding, RNAs (ncRNA) in the control of various cellular processes has greatly expanded researchers’ understanding of cellular genetics. Advances include insights into developing novel therapeutic strategies. As one example, tumor-suppressive ncRNAs that are depleted in carcinoma tissues may be reintroduced into cancer cells to manage tumor progression. Unfortunately, existing methods of ncRNA production - such as chemical synthesis - are very expensive and run the risk of altering the RNA’s structure and its associated biological activity. The lack of an efficient method for producing large quantities of inexpensive, naturally-occurring and biologically-functional ncRNA agents hinders basic research on ncRNA structures. It also limits potentially critical, translational research on ncRNA-based therapies.
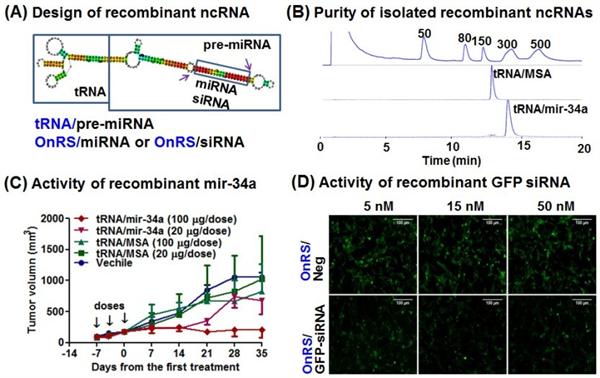
Researchers at the University of California, Davis have developed a method to cost-effectively design, produce, and purify large amounts of chimeric, non-coding, RNA agents using recombinant RNA technology. This method involves using E.coli and tRNA scaffolding. This production approach allows for high levels of ncRNA expression and stability in a recombinant host cell. The resulting ncRNA can be purified with high homogeneity, and used to help control biological processes. The ncRNA can also become a “stealth” carrier for the delivery of therapeutic RNA agents or RNA biomarkers.
Applications
• Increases availability of ncRNA for basic and translational research
• Potential carrier of biomarkers or therapeutics
Features/Benefits
• Provides a source of inexpensive, high-purity, ncRNA
• Increases opportunities for the delivery of therapeutic or biomarkers using stealth RNA carriers
Patent Status
| Country | Type | Number | Dated | Case |
| United States Of America | Issued Patent | 10,619,156 | 04/14/2020 | 2014-279 |
Contact
- Pooja N. Bhayani
- pnbhayani@ucdavis.edu
- tel: View Phone Number.
Inventors
- Chen, Qiuxia
- Li, Meimei
- Wang, Weipeng
- Yu, Aiming
Other Information
Keywords
Biomarkers, Chimeric RNA, E. coli, RNA delivery, RNA production, RNA purification, Therapeutics
