Magnetometer Based On Spin Wave Interferometer
Patent Status
| Country | Type | Number | Dated | Case |
| United States Of America | Issued Patent | 11,243,276 | 02/08/2022 | 2017-150 |
Full Description
Background
Magnetometers are among the most widely used instruments for a variety of applications. Sensitivity, intrinsic noise, size, energy budget and cost are the important characteristics of magnetometers. A variety of magnetic sensors, in currently available magnetometers, are available based on their unique advantages and the intended application. Some of the highly sensitive magnetometers are plagued by high cost and require cryogenic temperatures for operation. The cheaper magnetometers are also less sensitive. These challenges continue to hinder practical application of magnetometers for a wide variety of uses.
Current Invention
Prof. Aleksandr Khitun has developed a patent pending, novel magnetometer based on spin wave interferometer. The sensing element for this instrument consists of a magnetic cross junction with four micro-antennas fabricated at the edges. Two of these antennas are used for spin wave excitation and the other two are used for detection of the inductive voltages generated by the interference of the spin waves. The output voltage attains its maximum or minimum depending on if the spin waves are coming in phase (constructive interference) or out of phase (destructive interference), respectively. The maximum sensitivity is during destructive interference.
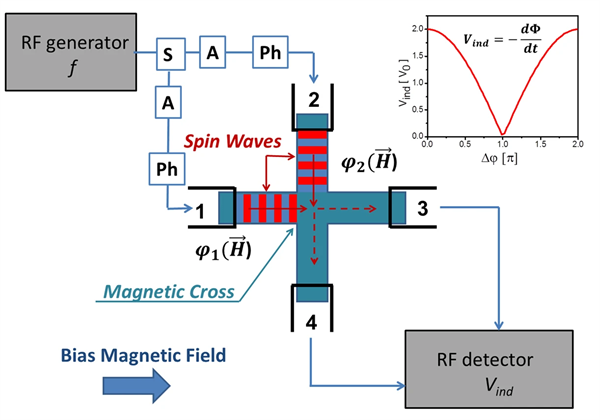
Schematics of the sensing element – a spin wave interferometer built on a magnetic cross junction.
Advantages
The significance and benefits of this innovation are:
Suggested uses
- Tracking distant objects such as submarines (1 – 10 km)
- Tracking small objects such as weapons (at 50 m)
- Detecting electromagnetic impulses in the brain
- Gas pipeline monitoring.
- Space telescopes
State Of Development
Lab level prototype built and tested
Inventions by Aleksandr Khitun
All inventions by Aleksandr Khitun
Related Materials
Contact
- Venkata S. Krishnamurty
- venkata.krishnamurty@ucr.edu
- tel: View Phone Number.
Other Information
Keywords
Magnetic sensor, Spin wave interferometer, Submarine tracking, Tracking and detecting, Brain impulse monitoring, Gas pipeline monitoring, Space telescopes
