Carbon Nanotube Infrared Detector
Patent Status
| Country | Type | Number | Dated | Case |
| United States Of America | Issued Patent | 7,723,684 | 05/25/2010 | 2006-367 |
Full Description
Background
Prominent adsorption features and photoconductivity of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) suggest an outstanding potential for application in nanoscale sized optoelectronic applications. The extremely large photo response that is observed for suspended SWNT films also makes them attractive candidates for sensitive element of an infrared bolometer. A high negative value of temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) of the bolometer sensitive element is required to efficiently transfer temperature modulation into an electrical signal.
Current Invention
Researchers led by Prof. Robert Haddon at UCR have developed a patented, novel infrared bolometer derived from their research on the photoconductivity of semi-transparent SWNTs. In their invention, the SWNT film was suspended between two blocks that also served as electrical contacts. In suspending the SWNT film in vacuum they show that they can increase the photoconductivity response by at least 5 orders of magnitude.
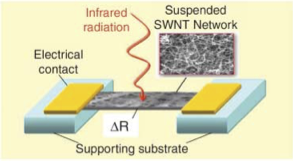
Schematic diagram of SWNT network suspended between electrical contacts.
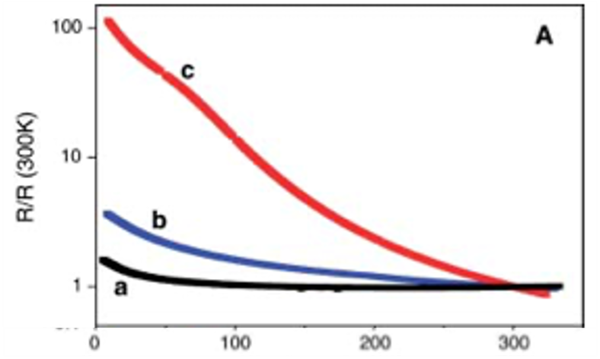
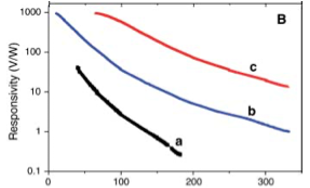
Temperature dependence of (A) resistance and (B) voltage responsivity – of 3 SWNT films (a) 1 micron thick purified SWNTs, (b) 100 nm thick purified SWNTs annealed in vacuum and (c) 40 nm thick purified SWNTs annealed in vacuum.
Advantages
The significance and benefits of their invention are:
Suggested uses
Suitable applications for this innovation include:
Related Materials
Inventions by Prof. Robert Haddon
Please see all inventions by Prof. Robert Haddon and his team at UCR
Contact
- Venkata S. Krishnamurty
- venkata.krishnamurty@ucr.edu
- tel: View Phone Number.
Other Information
Keywords
Bolometer, Infrared detector, Carbon nanotubes, Sensors and detectors
