Neuro-Swarm3: System-On-A-Nanoparticle For Wireless Recording Of Brain Activity
Background
The recent discovery of genetically encoded voltage sensitive fluorescence indicators (GEVI) has created tremendous excitement as light offers unparalleled multiplexing and information carrying capabilities. However, GEVI cannot be used in humans as it requires expression of voltage sensitive molecules by neurons and therefore genetic manipulation. In addition, attenuation of visible light in biological tissue renders much of the brain inaccessable to fluorescence based techniques.
Technology Description
Neuro-SWARM3 uses optical excitation power transfer and signal readout primarily useful as a contrast agent for sensing the electrical field produced by neurons.
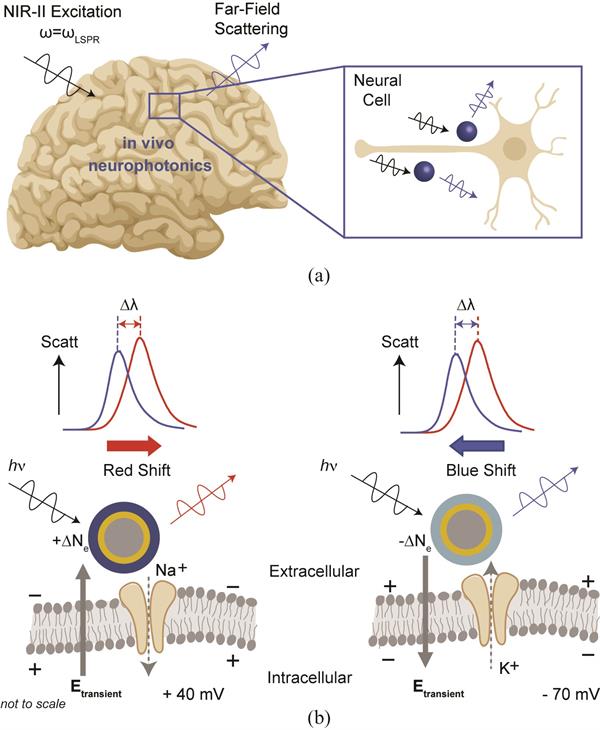
Neuro-SWARM3 enables direct measurement of local electric field dynamics through near infrared light via localized surface plasmon enhanced scattering and electro-optic sensitivity to local electric-field dynamics, primarily through electrochromic loading of PEDOT:PSS.
NeuroSWARM3 can be made with a dielectric (silica, SiO2) and magnetic (magnetite, Fe3O4) core, covered by a metallic (gold) shell, an electrochromic polymer (PEDOT) coat, and an optional surface functionalization with, for example, lipids or antibodies. This technology can also work with a semiconductor core, but methods to produce semiconductor nanoparticles which are uniform in shape and distribution remain elusive1.
The layers of NeuroSWARM3
can be altered to change the wavelength used for optical sensing, but it is
originally designed for near infrared wavelengths with dimensions of
silica-gold-PEDOT layers totaling less than 200 nanometers in diameter.
Applications
Neurophysiology research
Diagnostics of brain diseases
Brain research
Diagnostic imaging
Biological electrochemical systems
Advantages
(1) it enables use of infrared light within the biologically transparent near infrared (NIR-II, 1000-1700 nm) window for direct read-out through the skull,
(2)it circumvents invasive surgical operations since no wiring or power supply is needed for the wireless electroplasmonic excitation and remote detection backscattering signal,
(3)due to its nanoscale dimensions (< 200 nm) comparable to viral particles, NeuroSWARM can be delivered to brain tissue through the blood or cerebrospinal fluid,
(4) as the electro-plasmonic signal conversion removes front-end signal processing requirements and enables optical read-out, it opens the door to large scale in vivo measurements that are not restricted by electrode dimensions, wiring, or electronic bandwidth limitations,
(5) by being much smaller than the critical dimensions that trigger glial cell response (~ 12 μm),it offers a long term operation capability.
Intellectual Property Information
| Country | Type | Number | Dated | Case |
| United States Of America | Published Application | 20240268746 | 08/15/2024 | 2021-984 |
Related Materials
Contact
- Marc Oettinger
- marc.oettinger@ucsc.edu
- tel: View Phone Number.
Inventors
- Habib, Ahsan
- Hardy, Neil
- Yanik, Ahmet
Other Information
Keywords
Nanoparticle, Noninvasive electrophysiological measurement, Neuroscience, Near-infrared, Optically detectable
