Hybrid Nanostructured Materials For Rechargeable Energy Storage Technologies
Full Description
Background
Graphitic anodes in current Lithium-ion batteries (LIB) are limited to theoretical capacity of 372 mAh/gram. Silicon based anodes are identified to be the next generation for LIBs due to their theoretical capacity limit of 4200 mAh/gram. Obstacles that delay the adoption of Lithium-Silicon batteries are:
- Significant increase in volume of the silicon anode during alloying and de-alloying process.
- Large solid electrolyte interface layer that quickly kill the performance of the electrode.
Current Invention
In this patented technology, UCR research team led by Prof. Cengiz Ozkan describe an innovative, 3-dimensional silicon decorated Cone shaped Carbon nanotube Clusters (Si-CCC) architecture and its application as LIB anode. The pillared carbon nanotubes (CNT) and graphene nanostructure are grown by a 2-step, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process on a copper foil – which is a commonly used current collector in batteries. Button type half cells, with Si-CCC anodes and Lithium metal cathodes, were assembled and tested. The cells achieved a very high, fully reversible capacity of 1,644.4 mAh/gram. After 230 charge-discharge cycles, the cells had a capacity of 1050 mAh/gram and exhibited 100% coulombic efficiency.
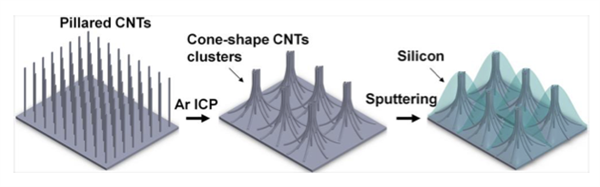
Synthesis of silicon decorated, cone shaped CNT clusters
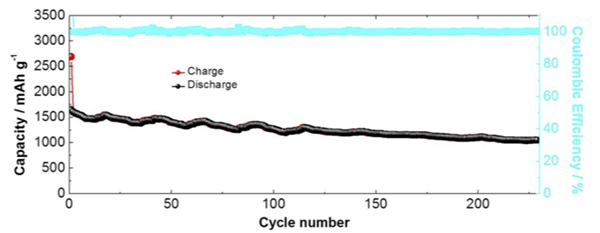
Cycling performance and coulombic efficiency of the PGN electrode at a current density of 1000 mA/gram
Advantages
The advantages of this invention are:
Suggested uses
- Lithium-Ion Batteries.
- Electrochemical energy storage devices.
Related Materials
Patent Status
| Country | Type | Number | Dated | Case |
| United States Of America | Issued Patent | 10,211,448 | 02/19/2019 | 2014-173 |
Contact
- Venkata S. Krishnamurty
- venkata.krishnamurty@ucr.edu
- tel: View Phone Number.
Other Information
Keywords
Lithium ion battery, Energy storage, Lithium silicon, Carbon Nanotube, Silicon carbon cluster, Graphene
