Nanostructured Ink Material For Electronic And Energy Storage Devices And Methods Of Making And Using Thereof
Full Description
Background
Ultrafast charging, high discharge rates and long cycle life make supercapacitors a valuable energy storage device. Their lower energy densities in comparison to batteries preclude their standalone usage in applications that require prolonged energy discharge. Boosting the energy density and power density of supercapacitors would be of importance for their adoption in applications such as Electric Vehicles. Boosting of both energy, power density and long cycle life can be achieved by parameters such as high capacitance, large surface area, short ion diffusion pathways, excellent interfacial integrity and operational voltage window.
Current Invention
UCR research team has developed a patented technology for such a supercapacitor with higher energy and power density. Their simple invention is an electrode with a 3-dimensional, sub-5 nanometer, hydrous Ruthenium Oxide (RuO2) anchored graphene and carbon nanotube hybrid foam (RGM) architecture.

Schematic illustration of the preparation process of RGM foam and SEM images showing the as grown foam and different loading of RGM.
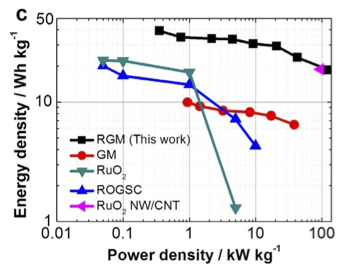
Ragone plot related to energy density and power density of packaged whole cell RGM supercapacitor.
Advantages
The significance of their discovery is defined by:
Suggested uses
- Supercapacitors.
- Energy storage devices.
Related Materials
Patent Status
| Country | Type | Number | Dated | Case |
| United States Of America | Issued Patent | 10,580,591 | 03/03/2020 | 2013-407 |
| United States Of America | Issued Patent | 10,163,583 | 12/25/2018 | 2013-406 |
Contact
- Venkata S. Krishnamurty
- venkata.krishnamurty@ucr.edu
- tel: View Phone Number.
Other Information
Keywords
Supercapacitor, Energy storage, Electrochemistry, Nanotechnology, Carbon materials, Ruthenium Oxide, Energy density, Power density
