Piezoelectric Scaffold Material and Its In Vivo Activation For Nerve Regeneration
Tech ID: 34409 / UC Case 2018-276-0
Background
Severe injuries to the peripheral nervous system present a significant clinical problem due to limited or total lack of treatment options for fully functional recovery. Considering that recent estimates state that over 20 million Americans suffer from peripheral neuropathy due to nerve damage in the extremities, there is an unmet need for a nerve repair device that can non-invasively promote the regeneration of all necessary neural cell types to achieve functional recovery.
Brief Description
Professor Jin Nam and colleagues from the University of California, Riverside have developed novel synthesize piezoelectric scaffolds that can be remotely activated without a physically connected electrical wire to produce optimal electric fields in vivo for enhanced nerve regeneration. The technology works by using a biocompatible nanofibrous scaffold with a mesh-like structure that mimics the body’s natural tissue architecture and is made from piezoelectric materials. This technology allows for the mechano-electrical stimulation (MES) on endogenous or transplanted stem cells to enhance their neural differentiation/maturation. This technology is advantageous because this scaffold can be applied as a conduit or patch and activated remotely and non-invasively.
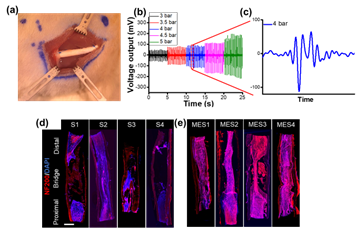
Fig 1: In vivo characterization of piezoelectric conduits and their impact on sciatic nerve regeneration. (a) A photo showing the transplantation of the P(VDF-TrFE) conduit
into the rat to bridge the sciatic nerve gap. (b) Shockwave magnitude-dependent voltage outputs from P(VDF-TrFE) conduits. (c) A zoomed-in voltage output graph showing the generation of 200 mVp-p under the 4-bar pressure of the shockwave actuation. (d, e) Large-field-of-view immunofluorescence images showing the entire structure of
P(VDF-TrFE) conduit and ingrowth tissue, bridging transected sciatic nerve in (d) static and (e) MES conditions (NF200: axonal marker NF200; S1-S4 denote each of the 4 rats in the static group while MES1-MES4 denote each of the 4 rats from the MES group).
Suggested uses
- For use in regenerative medicine to promote neural repair by enhancing nerve growth, connectivity, and myelin development.
- For the development of piezoelectric neuro conduit guide scaffolds for nerve regeneration and repair.
Patent Status
Patent Pending
Related Materials
Contact
- Grace Yee
- grace.yee@ucr.edu
- tel: View Phone Number.
Other Information
Keywords
Piezoelectric Material, Mechano-Electrical Stimulation, Nerve Regeneration, Nerve Conduit, Neural Stem Cells (NSCs), In Vitro Nerve Models, Neural Tissue Engineering
