Methods For Generating Target Enrichment Probes For Genome Sequencing Applications
Background
Hybridization capture approaches allow targeted high-throughput sequencing analysis at reduced costs compared to shotgun sequencing. Hybridization capture is particularly useful in analyses of genomic data from ancient, environmental, and forensic samples, where target content is low, DNA is fragmented and multiplex PCR or other targeted approaches often fail. Hybridization capture involves the use of "bait" nucleotides that capture genomic sequences that are of particular interest for the researcher.
Current bait synthesis methods require large-scale oligonucleotide chemical synthesis and/or in vitro transcription. Both RNA and DNA bait generation requires synthesizing template oligonucleotides using phosphoramidite chemistry. Microarray-based synthesis generates oligonucleotides in femtomole scales with high chemical coupling error rates. Templates synthesized at small-scale require enzymatic amplification before use in hybridization capture.
The solution proposed here involves a simple and highly efficient method to generate target probes using isothermal amplification. Target sequences are circularized and then amplified by rolling circle amplification. This method generates concatemers comprising thousands of copies of the target seqeuence. Restriction digestion of the amplified product then produces probes to use in target enrichment applications.
Technology Description
This is a cost-effective, large-scale DNA bait synthesis method that we call Circular Nucleic acid Enrichment Reagent, or CNER (pronounced as snare). The CNER method involves circularization of target template oligos that contain a linker region to promote circularization via splint-ligation and a rare-cutter restriction enzyme site for subsequent discretization of the capture probes. Circularized templates are isothermally amplified by rolling circle amplification (RCA) with the inclusion of biotinylated nucleotides. The long RCA products are discretized into single biotinylated baits by restriction digestion. The resulting biotinylated CNER probes can be generated in microgram quantities and used for capture enrichments on streptavidin-coated beads.
Figure:
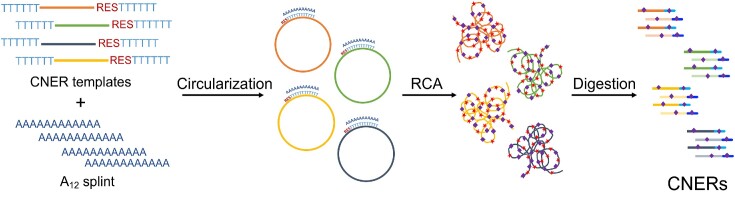
Circular Nucleic acid Enrichment Reagent method. An oligonucleotide template pool containing restriction enzyme recognition sites (RES) and oligo-dT linkers is circularized by an oligo-dA splint adapter mediated ligation. Circularized templates are isothermally amplified using oligo-dA and oligo-dT oligos by rolling circle amplification (RCA). RCA products are then digested with restriction enzymes to generate CNERs. CNERs generate both strands (dark and light shades of colors) of the templates. Biotinylated nucleotides (purple diamonds) are incorporated during amplification.
Applications
- Generation of hybridization capture probes
- Targeted high throughput genomic sequencing
Advantages
- Low cost hybridization capture probes +
- Targeted high throughput seqeuncing =
- Significantly lower cost genomic sequencing
- Add barcodes and cost drops still lower
Intellectual Property Information
| Country | Type | Number | Dated | Case |
| European Patent Office | Published Application | 4078596 | 10/26/2022 | 2019-747 |
| India | Published Application | 202247036287 A | 07/01/2022 | 2019-747 |
Additional Patent Pending
Related Materials
Contact
- Jeff M. Jackson
- jjackso6@ucsc.edu
- tel: View Phone Number.
Inventors
- Green, Richard E.
- Sundararaman, Balaji
Other Information
Keywords
Nucleic acid sequencing, Genomic Sequencing, Target enrichment, Hybridization Capture, Bait probes, Nucleic acid probes, Rolling circle amplification, Hybridization capture probes, Low cost hybridization capture probes, High throughput sequencing
