Stochastic Route Planning For Electric Vehicles
Patent Status
| Country | Type | Number | Dated | Case |
| United States Of America | Issued Patent | 12,392,624 | 08/19/2025 | 2022-888 |
Full Description
Background
Standard electric vehicle (EV) routing models seek to minimize travel time while maintaining a non-zero state of charge (SoC) of the battery, along the route. Most formulations also assume that travel times and energy consumption can be precisely determined. In reality, both travel time and energy consumption are variable (stochastic) and difficult to estimate reliably. Stochastic routing algorithms model transit times along the roads (edges) as variables with given probability distributions. Since stochastic routing algorithms are typically computationally slower, recent formulations have made certain unrealistic assumptions for the probability distribution of travel times and energy consumption.
Technology
Prof. Ravishankar and his team at UC Riverside have developed a novel, stochastic route planning algorithm. Their approach finds an optimal route for an EV, so that the travel time and energy consumption along the route satisfy required constraints. The intent of the optimization is to ensure that the EV reaches the destination without being stranded while satisfying the travel constraints due to SoC of the battery. The algorithm takes into account several criteria including travel time, elevation, location of charging stations, battery SoC, duration and amount of charging required to provide a realistic route for the vehicle.
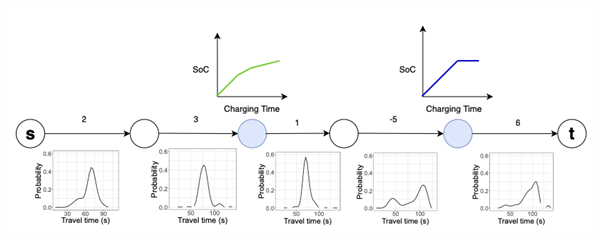
Schematic illuatration of the EV navigation algorithm. The roads have two weights - a travel time distribution (below) and an expected energy depletion or charging (above).
Advantages
The novel aspects of this invention are:
- Provides an accurate and realistic route that ensures that the driver is not stranded due to a lack of battery charge.
- Balanced planning of travel time and charging duration along the route.
- Accounts for significant variables during the travel including travel time, battery SoC, elevation (along the route), wind resistance, location of charging stations, charging duration, regenerative breaking, etc.
- Incorporates realistic and informed distribution of travel time, vehicle speed and energy consumption.
- An informed and comprehensive model for energy consumption along the route.
Suggested uses
EV route planning for:
- Delivery and fleet vehicles
- Route planners
- Personal and public transportation
- Traffic simulation
State Of Development
The team has developed a lab level prototype and have tested it in the Los Angeles area.
Related Materials
Contact
- Venkata S. Krishnamurty
- venkata.krishnamurty@ucr.edu
- tel: View Phone Number.
Other Information
Keywords
electric vehicles, navigation, stochastic routing, route planning, delivery vehicles, fleet vehicles, transportation
