Catalysts For Aqueous Contaminant Reduction
Patent Status
| Country | Type | Number | Dated | Case |
| United States Of America | Published Application | 2024-010050 | 03/28/2024 | 2022-897 |
Full Description
Background
In the US, the health reference level for chlorate (ClO3-) is set at 0.21 milligrams per liter (mg/L) and the minimum reporting level at 0.02 mg/L. Although ClO3- contamination challenge for water systems has been recognized, research efforts for ClO3- reduction are limited. Platinum group metal (PGM) catalyzed hydrogenation provides a clean degradation route. However, most reported ClO3- reduction catalysts exhibit maximum activity in acidic conditions or require higher dosage (10 - 80X) of the catalyst.
Technology
Prof. Jinyong Liu and his research team have developed a novel catalyst through the use of rational chemistry and simple engineering approach. The developed ruthenium (Ru) on palladium-carbon supports (Pd/C) makes it possible to treat ClO3- contamination under various water conditions. The facile method yields catalysts that demonstrat robustness and unprecedented performance.
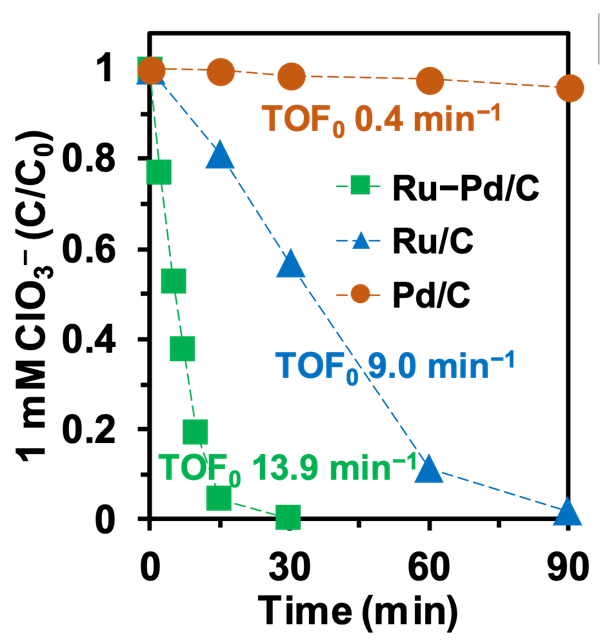
Profiles and turnover factor (TOF0) for 1 millimolar (mM) ClO3- reduction by three different catalysts.
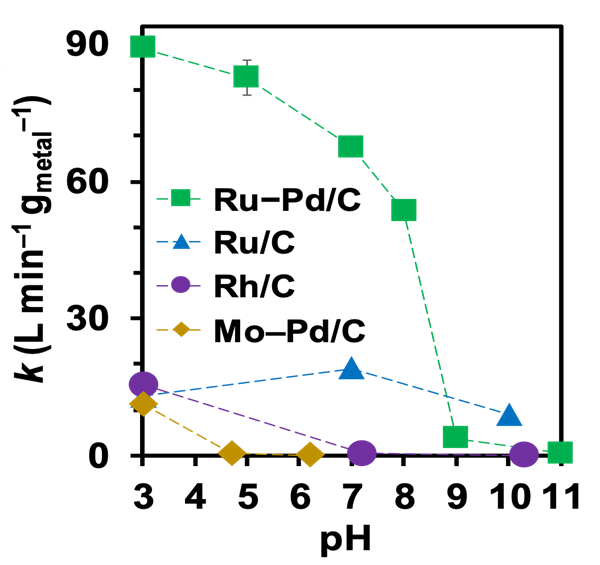
pH dependence of the Ru-Pd/C, Ru/C. First-order rate constants are normalized by the loading of PGM.
Advantages
- Facile catalyst preparation - a highly active catalyst is prepared in 20 minutes using 1 atmosphere H2 at 20 deg. C - without any heating.
- Unprecedented catalyst performance - the catalysts show a substantially higher activity of reduction at both neutral and acidic pH.
- Higher robustness - the catalyst allows complete reduction of ClO3- even in the presence of sulphate (SO42-) and chloride (Cl-).
- The ruthenium and palladium exhibit bimetallic synergy.
- Reduced cost of catalyst.
Suggested uses
Water treatment applications such as:
- Drinking water
- Waste-water runoffs from agriculture and dairy
- Waste-water treatment in industrial processes
- Water treatments that use various electrochemical processes
Related Materials
Inventor Information
- Please read recent press coverage of Prof. Jinyong Liu's research.
- Please visit Prof. Jinyong Liu's group website to learn more about their research.
- Please review all inventions by Prof. Jinyong Liu and his team at UCR
Contact
- Venkata S. Krishnamurty
- venkata.krishnamurty@ucr.edu
- tel: View Phone Number.
Other Information
Keywords
perchlorate, chlorate, chlorate contamination, catalyst, platinum group metals, ruthenium, palladium, water treatment, wastewater
