Lower Cost Method for Fabricating Porous Metal Oxide Composites
Background
Wastewater pollution generated by industrial processes such as manufacturing and transportation are a huge cause for concern. Due to this, businesses are facing greater pressure to conduct their activities in an environmentally-friendly manner. Of particular importance is the treatment of wastewater to eliminate contaminants.
Lower-cost methods for the controlled synthesis of metal oxides (including size, phase, morphology etc.), and synthesis of metal-oxide bulk composites for applications such as wastewater treatment are desirable.
Brief Description
Researchers at the University of California, Riverside have developed lower cost methods to synthesize metal oxide composites. The metal organic particles are fabricated by first dispersing a metal oxide precursor with a dispersing agent. The pH of the dispersing agent is set between 7.8 and 11. These conditions promote binding of the metal oxide and dispersing agent in solution. The resulting mixture is then heated at lower temperatures than current processes and subsequently extruded to form the desired geometry. The nanoparticles can be recovered and reused for further treatment. Metal oxides can also be fabricated into stand-alone structures, eliminating the need for nanoparticle recovery.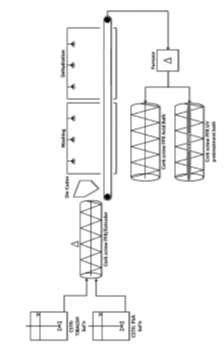
Fig. 1 Continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR) fabrication method for the metal oxide particles. Metal oxide is mixed with the dispersing agent, then washed, heat-treated and finally extruded into the desired geometry

Fig. 2 Dried cubes of TiO2 mixed with PVA dispersing agent
Suggested uses
The metal oxide particles may be used for
- photocatalytic water purification; or
- the manufacture of solar panels
Patent Status
| Country | Type | Number | Dated | Case |
| United States Of America | Issued Patent | 9,593,027 | 03/14/2017 | 2012-533 |
Full Description
Contact
- Venkata S. Krishnamurty
- venkata.krishnamurty@ucr.edu
- tel: View Phone Number.
Other Information
Keywords
metal oxide, photocatalytic, TiO2, wastewater, water treatment, solar panels
