A Data-Driven Method To Transforming Conventional Power Quality (PQ) And Fault Recorder (FR) Wavform Measurements Into Synchro-Waveforms
Summary
This invention provides a data-driven method to time-synchronize waveform data from conventional power quality meters. The algorithm transforms non-synchronized measurements into synchro-waveforms. This is achieved without needed expensive hardware upgrades. The method first aligns event signatures from different meters and then calculates a synchronization operator to align the entire dataset. The process unlocks the potential of advanced monitoring and analysis of existing grid infrastructure.
Full Description
Problem
Power quality meters installed in power grids record valuable waveform data but they lack precise time synchronization. Without synchronization, the data cannot be used for applications which are critical for detailed grid analysis, fault detection, and ensuring grid stability. The alternative of retrofitting power meters with GPS hardware is both prohibitively expensive and logistically complex.
Solution
Prof. Hamed Mohsenian-Rad and his team at UCR have developed a novel, two-step computational method that processes data from non-synchronized power quality meters to transform them into a synchronized dataset. The resulting synchronized dataset is functionally equivalent to data from expensive, GPS enabled sensors. The two steps are:
- Event signature alignment, where an optimization algorithm identifies and aligns the unique signatures of power grid events as captured by different meters.
- Synchronization operator estimation, which uses the results from the alignment and estimates a precise synchronization operator between any two meters.
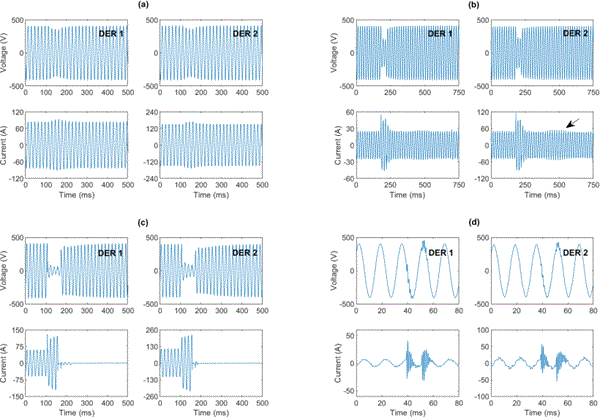
Application of time-synchronized waveform measurements in benchmarking the behavior of DERs on power distribution systems during: (a) a voltage sag; (b) a fault where the DERs managed to ride through the fault; (c) a fault where the DERs could not ride through the fault; and (d) sub-cycle oscillatios.
Advantages
- Cost-effective, as it eliminates the need for costly GPS hardware installation on legacy power meters.
- High accuracy - the method has been demonstrated to be accurate and robust and has been validated on real-world waveform measurements.
- Computationally efficient - the algorithm is designed for practical implementation and efficient processing of large datasets.
- Unlocks the value of data from already deployed power quality meters.
- Allows for the application to grid visibility, reliability and fault analysis.
Suggested uses
The technology is valuable for electric utilities, grid operators and data analytics companies focused on:
- Grid modernization
- Advanced power system monitoring and control
- Post-event fault analysis and location
- Improving grid stability and reliability
State Of Development
The method has been developed and successfully validated using real-world waveform data from operational power systems
Inventor Information
- Please read recent press coverage about Prof. Mohsenian-Rad at UCR
- Please visit Prof. Mohsenian-Rad's research website to learn more about his research
Related Materials
Patent Status
Patent Pending
Contact
- Venkata S. Krishnamurty
- venkata.krishnamurty@ucr.edu
- tel: View Phone Number.
Other Information
Keywords
smart grid, synchro-waveform, power quality, data analytics, grid modernization, waveform synchronization, power system monitoring
