Zinc-Iodine Battery with improved Coulombic efficiency
Background
Static Zn-I2 batteries (ZIBs) have been designed to overcome many hurdles of flow batteries. A remaining challenge is the self discharge caused by the shuttling of I3- ions to the zinc anode. This results in low Coulombic efficiency. Other strategies to address this challenge include physically blocking the I3- shuttling with an ion selective membrane (e.g. Nafion), but this increases the device cost and inner resistance. Another alternative is to encapsulate the I2 in microporous carbon and use another solution as an electrolyte. While this results in improved Coulombic efficiency, the total capacity and energy density are reduced.
Technology Description
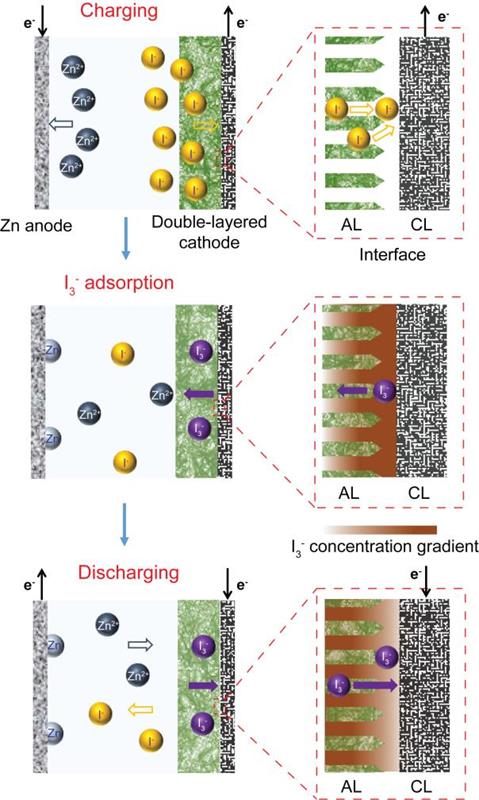
The solution to the problem was a double layered cathode that includes a conductive layer serves as a cathodic current collector and an adsorptive layer.
During charging, the oxidation of I- takes place at the interface between the conductive layer and the adsorptive layer. I- in the solution transfer electrons to the conductive layer and spontaneously form adsorbed I3- ions at the absorptive layer interface. Adsorbed I3- ions can diffuse into the bulk structure of the adsorptive layer following the concentration gradient and reexpose the adsorptive layer/conductive layer interface to collect newly formed I3- ions.
During discharge, adsorbed I3- ions will be reduced to I- ions at the interface between the conductive layer and the adsorptive layer.
So the presence of an adsorptive layer can suppress I3- shuttling and improve Coulombic efficiency without changing battery capacity.
In a proof of concept experiement, carbon cloth can be used as the conductive layer, while the adsorptive layer can be any of a number of materials including conducting polymers such as polypyrrole (PPy), polyaniline (PANi), and poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) as well as metallic comipounds.

Applications
Rechargeable batteries
Energy storage
Grid storage
Advantages
Improved Coulombic efficiency without loss of capacity
Intellectual Property Information
| Country | Type | Number | Dated | Case |
| United States Of America | Published Application | 20220336866 | 10/20/2022 | 2021-583 |
Additional Patent Pending
Related Materials
Contact
- Jeff M. Jackson
- jjackso6@ucsc.edu
- tel: View Phone Number.
Inventors
- Li, Yat
- Lin, Dun
Other Information
Keywords
Zinc based battery, Rechargeable battery, Aqueous rechargeable zinc based battery, Zinc-iodine, Zinc-iodine battery, Zinc-iodine redox flow battery, Coulombic efficiency, Double layered cathode
Categorized As
Additional Technologies by these Inventors
- Carbon-Doped NiO Catalyst For Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
- Z-Scheme Microbial Photoelectrochemical System (Mps) For Wastewater-To-Chemical Fuel Conversion
- Hydrogen-Treated Semiconductor Metal Oxides For Photoelectrochemical (PEC) Water Splitting
- Self-Biased and Sustainable Microbial Electrohydrogenesis Device
- Three-Dimensional Hierarchical Porous Carbon Foams For Supercapcitors
